dojox.app¶
| since: | V1.7 |
|---|
Implements application framework using dojox.mvc for web application on desktop/mobile platforms.
Introduction¶
dojox.app is an application frame work designed to allow simple configuration of nested scenes and views and to facilitate the transitioning between these views. It is similar in function to the dojox.mobile.app framework, but will not be limited to use on mobile devices. Applications for desktops, mobiles, and tablets will be configurable and buildable for easy and fast deployment. There are two core libraries that will need to work together to accomplish these goals
dojox.app - A library that provides high-level application controllers, defined by metadata which describes the overall structure and navigation of the application and it’s views.
dojox.mvc - A library that provides the ability to have view concerns separated from model or data concerns but have simple bindings or connections between them that can keep either side in sync, as well as respond to events or actions. The library also provides the ability to generate data-bound forms and views dynamically, built on key elements of mvc and app.
Overview¶
Application structure overview.
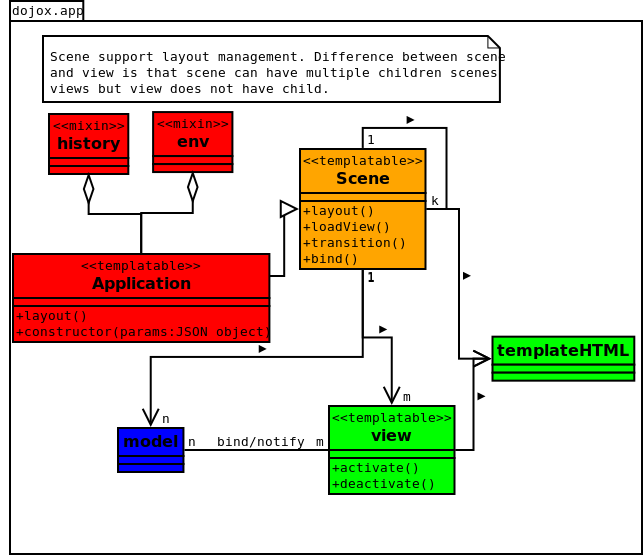
Components in dojox.app
dojox.app.view - dojox.app.view provides a view like dojox.mobile.View. It contains a template string which will be rendered with user defined template segments. A view should have no child view.
dojox.app.bind - dojox.app.bind is used to query dojox.mvc widgets, get and set binding data for each widgets with “ref” or data-dojo-props=”ref: xxx” tag. data-dojo-type, data-dojo-type, ref and data-dojo-props are compatible in a view.
dojox.app.model - dojox.app.model creates statefulModel data source with JSON data or dojo data store. The data model can be binded to a dojox.mvc widget by dojox.app.bind.
dojox.app.scene - dojox.app.scene is used to create the layout for each child view, manage the transition between views, resize layout to fit the display area. A scene can contains one or more children views or scenes. The difference between scene and view is that scene can have multiple children scenes views but view does not have child.
dojox.app.module.env - dojox.app.module.env provides dojo, dijit, dojox environment.
dojox.app.module.histroy - dojox.app.module.history manages transition forward and backward between views/scenes. A view can use ‘transitionOptions’ or ‘href’ to navigate forward or backward by utilizing HTML5 history API.
dojox.app.main - dojox.app.main(Application) is used to create a dojox.app application by the configuration in config.json. The main function includes: load configuration, load data from data source, create views, create data models, bind data models to views by dojox.app.bind, create scenes between views, parse application by dojo.parser.parse.
Usage¶
To create and startup a dojox.app application, a dojox.app configuration JSON is needed to initialize the application. Here are the necessary files to start an application. An html (index.html) is needed to load dojo.js and a javascript file included in index.html is used to create the application.
Index.html
<!-- load dojo.js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../../../dojo/dojo.js"></script>
<!-- load dojox.app startup file, the actual launcher -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="multiSceneApp.js"></script>
multiSceneApp.js
//Get current path
var path = window.location.pathname;
if(path.charAt(path.length)!="/"){
path = path.split("/");
path.pop();
path=path.join("/");
}
//register current application module path
dojo.registerModulePath("app", path);
//load configuration json file
require(["dojo/_base/html", "dojox/app/main", "dojo/text!app/config.json"], function(dojo, Application, config){
//startup the application
app = Application(eval("(" + config + ")"));
});
Application loads dojox.app configuration file and create view, scene, model with templateHTML. env provides dojo runtime environment for dojox.app and history cache users operation.
Here is the configuration instruction table.
| Configuration | Description |
| id | Id of dojox.app application |
| name | Name of dojox.app application |
| description | Description of dojox.app application |
| splash | Splash screen of dojox.app application (reserved but not implemented) |
| dependencies | Dependencies of dojox.app application. It can be defined as global dependencies for application or as view dependencies in a view. |
| modules | Modules for the application. These are basically used as the mixins in dojo.declare() for the application. They modify the top level behavior of the application, how it processes the config or any other life cycle |
| stores | Define dojo data stores which are used by dojox.app data model. A data store is composed by store name, store type and store parameters. |
| models | Models and instantiation parameters for the models including ‘type’ as a property allows one to override the class that will be used for the model. By default it is dojox.mvc.model. |
| defaultView | The name of the scene/view to load when the application is initialized. |
| defaultTransition | The default type of animation for the view transition. |
| views | The children views/scenes of the application or current scene. |
Sample¶
Sample application html page: index.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,maximum-scale=1,minimum-scale=1,user-scalable=no"/>
<meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" />
<title>Sample App</title>
<link href="../../../mobile/themes/iphone/base.css" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../../../dojo/dojo.js"></script>
<!-- the actual application launcher -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="sampleApp.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Sample application creation script: sampleApp.js
The actual configuration for the application is loaded by dojo/text module and is passed into call back as the “config” variable. Then the JSON string is resolved to JSON object and is used to create the application.
var path = window.location.pathname;
if(path.charAt(path.length)!="/"){
path = path.split("/");
path.pop();
path=path.join("/");
}
dojo.registerModulePath("app", path);
require(["dojo", "dojox/app/main", "dojo/text!app/config.json", "dojox/json/ref"], function(dojo, Application, config, ref){
app = Application(dojox.json.ref.fromJson(config));
});
Sample application configuration:
The application configuration json data is used to declare views, models and their relationship in the application. The application will control the views loading and views/models binding.
{
"id": "sampleApp",
"name": "Sample App",
"description": "A Sample App",
"splash": "splash",
//Dependencies for the application. The modules in the dependencies array object will be
//loaded before application is started.
"dependencies": [
"dojox/mobile/TabBar",
"dojox/mobile/RoundRect",
"dojox/mobile/TabBarButton",
"dojox/mobile/Button",
"dojox/mobile/RoundRect",
"dojox/mobile/Heading"
],
//stores we are using
"stores": {
"namesStore":{
"type": "dojo.store.Memory",
"params": { //parameters used to initialize the data store
"data": "modelApp.names"
}
},
"repeatStore":{
"type": "dojo.store.Memory",
"params": {
"data": "modelApp.repeatData"
}
}
},
//models and instantiation parameters for the models. Including 'type' as a property
// allows one to override the class that will be used for the model. By default it is
// dojox/mvc/model
// The model declared at application level will be initialized before application startup
// The model declared at scene/view level will be initialized before scene/view loaded
"models": {
"names": {
"params":{
"store": {"$ref":"#stores.namesStore"}
}
}
},
// Modules for the app. The are basically used as the second
// array of mixins in a dojo.declare(). Modify the top level behavior
// of the app, how it processes the config or any other life cycle
// by creating and including one or more of these
"modules": [
"dojox/app/module/env",
"dojox/app/module/history"
],
"template": "application.html",
//the name of the scene to load when the app is initialized.
"defaultView": "home",
//The default animation effect of transition between sub scenes and views of
// this application.
"defaultTransition": "slide",
//scenes are groups of views and models loaded at once
//scenes and view in the application all have access to application level models
"views": {
//simple view without any children views or scenes
//views can has its own dependencies which will be loaded
//before the view is first initialized.
"home": {
"type": "dojox.app.view",
"dependencies":[
"dojox/mobile/RoundRectList",
"dojox/mobile/ListItem",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeCategory"
],
"template": "views/simple/home.html"
},
//simple scene which loads all views and shows the default first
"main":{
//all views in the main scene will be bound to the user model
"models": [],
"type": "dojox.app.scene",
"template": "simple.html",
"defaultView": "main",
"defaultTransition": "slide",
//the views available to this scene
"views": {
"main":{
"template": "views/simple/main.html"
},
"second":{
"template": "views/simple/second.html"
},
"third":{
"template": "views/simple/third.html"
}
},
"dependencies":[
"dojox/mobile/RoundRectList",
"dojox/mobile/ListItem",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeCategory",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeList"
]
},
"repeat": {
"type": "dojox.app.view",
//model declared at scene/view level will be accessible to this scene/view
// or its children.
"models": {
"repeatmodels": {
"params":{
"store": {"$ref":"#stores.repeatStore"}
}
}
},
"template": "views/repeat.html",
"dependencies":["dojox/mobile/TextBox"]
}
}
}
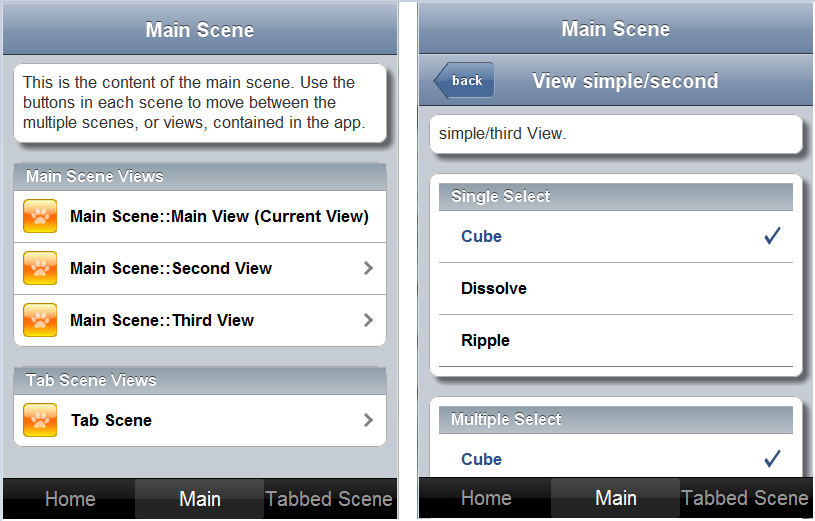
Sample render result
Comparison with dojox.mobile.app¶
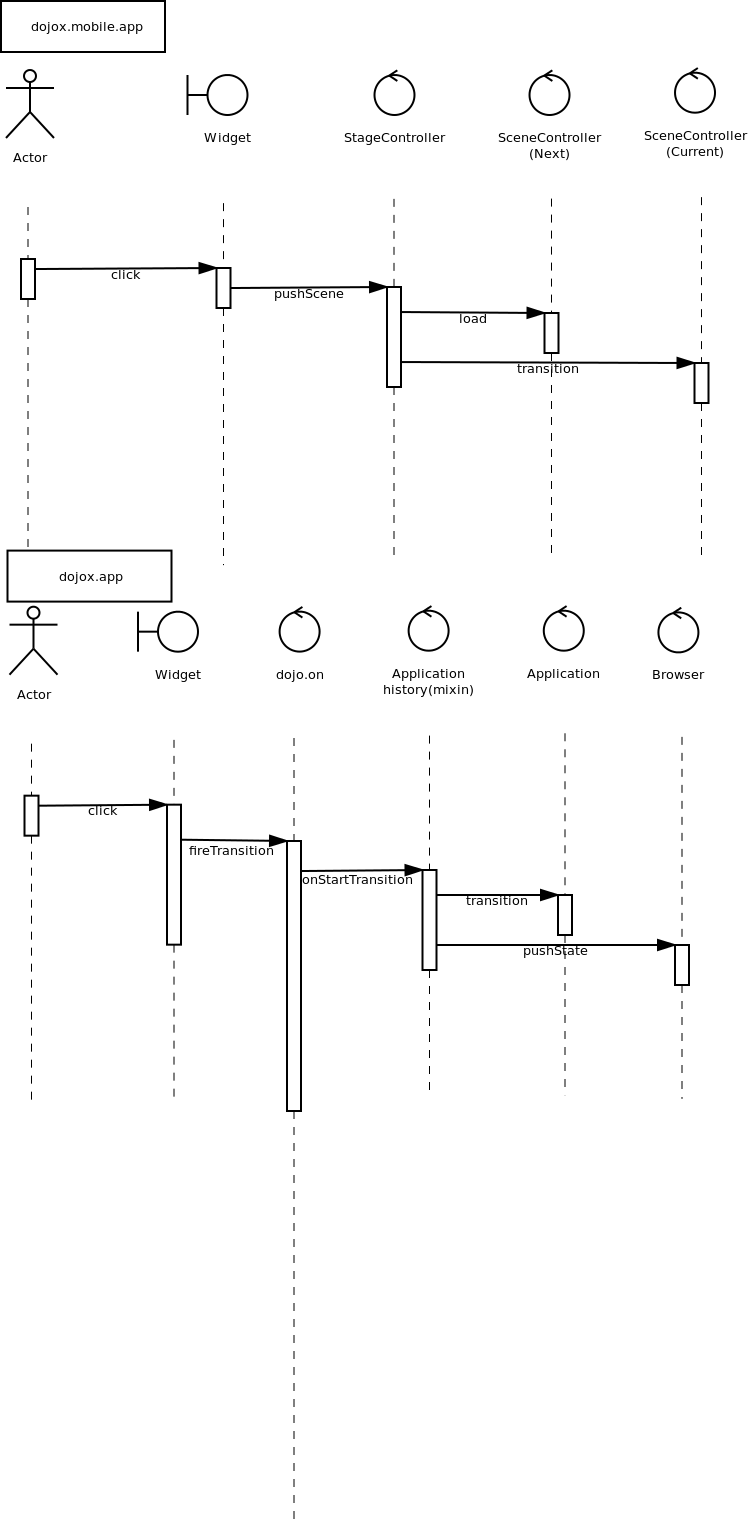
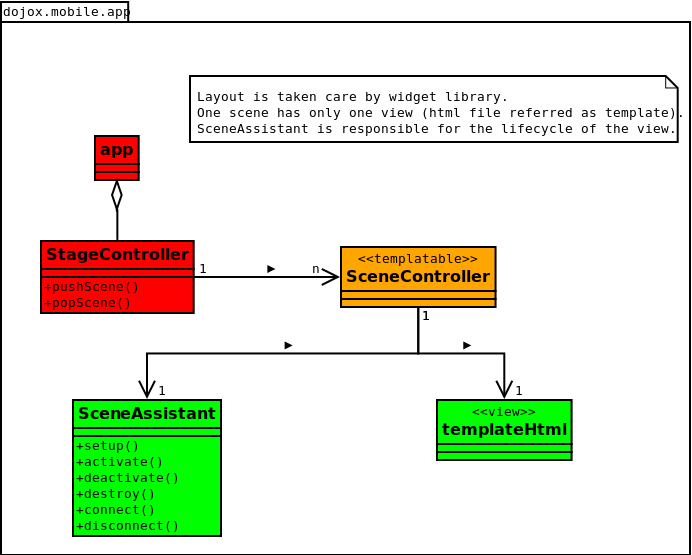
The main difference between dojox.app and dojox.mobile.app is listed as following. dojox.app enables the model binding dojox.app uses scene/view structure to enable the nested scene or view which resembles the composite design pattern. It does not mean dojox.mobile.app cannot do that but it needs coding to implement that. dojox.app contains the layout mechanism to ensure the content at different application/scene/view level work well together dojox.mobile.app manage the navigation history in StageController by using a history stack. dojox.app manage the navigation history through HTML5 pushState standard and delegate it to browser enabled history management.

Here is the sequence diagram to reflect the difference in the navigation management.