dojox/app¶
| since: | V1.7 |
|---|
Contents
Introduction¶
dojox/app is an application framework designed to simply configure through a configuration file an application formed of potentially nested views and to facilitate the transitioning between those views based. Its main current targets are mobile (phone & tablet) devices but it is not restricted to this and can be used for desktop applications as well. Thanks to dojox/app the applications are easily configurable and buildable for easy and fast deployment.
Creating an Application¶
As with any Dojo-based web application, it’s important to create your HTML page with a script tag referencing the Dojo
loader dojo. Once done you require the dojox/app main module and provide it with the application JSON configuration file as follows:
require(["dojox/app/main", "dojox/json/ref", "dojo/text!./config.json"],
function(Application, json, config){
// startup the application
Application(json.fromJson(config));
});
Upon loading the configuration, the views, stores and models described in the configuration are created and the application lifecycle is started. The main difference with a traditional Dojo application is that the application structure is defined from the configuration file.
Here is an excerpt of a typical configuration file:
{
"id": "todoApp",
"name": "ToDo App",
"description": "These is a ToDo sample application based on the Dojo Toolkit and provided under Dojo license.",
"loaderConfig": {
"paths": {
"todoApp": "../demos/todoApp"
}
},
"dependencies": [
"dojox/mobile/TabBar",
// ...
"dojox/mvc/at"
],
"modules": [
"todoApp/todoApp"
],
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/Load",
"dojox/app/controllers/Transition",
"dojox/app/controllers/Layout"
],
"stores": {
"listsDataStore":{
"type": "dojo/data/ItemFileWriteStore",
"params": {
"url": "./resources/data/lists.json"
}
},
// ...
},
"models": {
"listsmodel": {
"modelLoader": "dojox/app/utils/mvcModel",
"type": "dojox/mvc/EditStoreRefListController",
"params":{
"datastore": {"$ref":"#stores.listsDataStore"}
}
},
"allitemlistmodel": {
"modelLoader": "dojox/app/utils/mvcModel",
"type": "dojox/mvc/EditStoreRefListController",
"params":{
"datastore": {"$ref":"#stores.allitemlistStore"}
}
}
},
"defaultView": "items,ViewListTodoItemsByPriority",
"has" : {
"!phone" : {
"controller": "todoApp/tablet/ViewTodoLists.js",
"template": "todoApp/tablet/ViewTodoLists.html"
},
"ie9orLess" : {
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/HistoryHash"
]
},
"!ie9orLess" : {
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/History"
]
}
},
"defaultTransition": "slide",
"views": {
"configuration": {
"defaultView": "SelectTodoList",
"defaultTransition": "slide",
"views": {
"SelectTodoList": {
"controller": "todoApp/configuration/SelectTodoList.js",
"template": "todoApp/configuration/SelectTodoList.html",
"nls": "todoApp/nls/SelectTodoList"
},
"ModifyTodoLists": {
"controller": "todoApp/configuration/ModifyTodoLists.js",
"template": "todoApp/configuration/ModifyTodoLists.html",
"nls": "todoApp/nls/ModifyTodoList"
},
"EditTodoList": {
"controller": "todoApp/configuration/EditTodoList.js",
"template": "todoApp/configuration/EditTodoList.html",
"nls": "todoApp/nls/EditTodoList"
}
}
},
// ...
}
}
You can find the entire configuration file for this typical application here
Once started the corresponding application looks like the following:

See the todoApp example in Dojo demos installation directory for the full application, or you can find it on github
Building an Application¶
Once you have created your configuration file and the application, you might want to build the application for production.
In order to help you build your application from the
configuration file dojox/app comes with extensions to the Dojo build system.
The first step is to create a simple Dojo build system profile that will contain the key
information of your build and import the dojox/app extensions into the build process as shown below (see require line in the profile):
// import the dojox/app extension to the build system
require(["dojox/app/build/buildControlApp"], function(bc){
});
var profile = {
basePath: "..",
releaseDir: "./layoutApp/release",
action: "release",
cssOptimize: "comments",
/* multipleAppConfigLayers: true,*/
packages:[{
name: "dojo",
location: "../../../dojo"
},{
name: "dijit",
location: "../../../dijit"
},{
name: "dojox",
location: "../../../dojox"
},{
name: "myApp",
location: "../../../myApp",
}],
layers: {
"myApp/myApp": {
include: [ "myApp/index.html" ]
}
}
};
You will then need to reference that profile as well as your configuration file when running the Dojo build tool. For example, from <dojo-install>/util/buildscript:
./build.sh --profile <dojo-install>/dojox/app/tests/layoutApp/build.profile.js
--appConfigFile <dojo-install>/dojox/app/tests/layoutApp/config.json
By default the extension uses the only layer in the profile (here “myApp/myApp”) to bundle all the modules for the application. You can specify an alternate layer you want to target by passing –appConfigLayer layer/name on the command line like this:
./build.sh --profile <dojo-install>/dojox/app/tests/layoutApp/build.profile.js
--appConfigFile <dojo-install>/dojox/app/tests/layoutApp/config.json
--appConfigLayer layer/name
Alternatively, you can make sure a layer per-view is built instead of a single layer for the entire application by having the multipleAppConfigLayers property set to true in your profile. This is useful if you have a lot of views that won’t get navigated to in a typical usage of your application. In that case you might not want to load everything upfront. In this case the controller file of each view will be used as the layer for the view.
Limitation
This extension does not support the ”./” shortcut notation to reference the modules in the config file and default controller file. You have to explicitly list your controller file and use absolute module paths. You can very easily do that by creating an “myApp” module that you should instead of ”.” to reference your modules.
The Configuration File¶
The configuration comes in the form of a JSON-like object of the following keys and property values:
id¶
String. Mandatory. The dojox/app application’s id. A global variable with id’s name is created by dojox/app/main.
id: "sampleApp"
description¶
String. Optional. The description of the dojox/app application
description: "Sample application that does what is needed"
loaderConfig¶
Object. Optional. Dependencies, modules and controllers are loaded using the Dojo AMD loader. This parameter allows to configure the loader itself and specify for example where custom modules can be found. See http://livedocs.dojotoolkit.org/loader/amd#module-identifiers
"loaderConfig" : {
"paths": {
"mypackage" : "can/be/found/here"
}
}
transit¶
AMD module identifier. Optional. By default dojox/app is using dojox/css3/transit module to perform transition animations. You can provide your own transition animation function by referencing it here:
"transit" : "my/app/transit"
The module should return a function with the following signature:
function(fromDomNode, toDomNode, transitionOptions){ }
and should return a promise.
dependencies¶
Array of AMD modules identifiers. Optional. When defined at the top level dependencies of the dojox/app application, these app level dependencies could also be added to the define for the app or one of the “modules” which are mixed into the app. When defined at view level, dependencies for the view.
"dependencies": [
"dojox/mobile/TabBar",
"dojox/mobile/RoundRect",
"dojox/mobile/TabBarButton",
"dojox/mobile/Button",
"dojox/mobile/RoundRect",
"dojox/mobile/Heading"
]
These are typically modules that are not required by the JavaScript module of the application or the view but that are still needed by the application or the view. Examples are the store or MVC modules or the modules needed by the markup of the view. If the application is using the full Dojo parser it does not necessarily need to list the markup dependencies as the parser will auto-require them.
modules¶
Array of AMD modules identifiers. Optional. Modules for the application. Used as the mixins when declaring the Application class in dojox/app/main. They modify the top level behavior of the application, how it processes the config, or any other life cycle. The “dojox/app/module/lifecycle” is automatically mixed into the application you don’t have the explicitly include it.
"modules": [
"mypackage/custom/module"
]
They are automatically added to the list of dependencies and as such do not need to be listed in the dependencies property.
controllers¶
Array of AMD modules identifiers. Mandatory. Controllers for the application. All the controllers listed here will be loaded during application startup to respond to application events and controller the application logic. In the previous release the “dojox/app/controllers/Load”, “dojox/app/controllers/Transition” and “dojox/app/controllers/Layout” were automatically mixed into the application, that is no longer the case, with 1.9 you must have them listed to include them.
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/Load",
"dojox/app/controllers/Transition",
"dojox/app/controllers/Layout"
],
They are automatically added to the list of dependencies and as such do not need to be listed in the dependencies property.
stores¶
Object. Optional. Dojo stores which are used by dojox/app to setup data models. A store item is an object with a a type and a params property. The type property is the AMD module identifier for the store class to be instantiated. The content of the params property is passed to the store class constructor to build an instance. Setting “observable”: true on a store will have the store wrapped in a dojo/store/Observable, but in order to use dojo/store/Observable it must be included in the dependencies section.
"stores": {
"store1":{
"type": "dojo/store/Memory",
"observable": true,
"params": { // parameters used to initialize the data store
"data": "modelApp.names"
}
},
"store2":{
"type": "dojo/store/JsonRest",
"params": {
"data": "modelApp.repeatData"
}
}
}
All stores modules that are used must also be explicitly listed in the dependencies property.
template¶
String. Mandatory for default views. HTML file. When defined at application level defines the application root template. When defined at view level defined the view template.
"template": "application.html"
models¶
Object. Optional. Models and their instantiation parameters. A model item is an object with three properties: the model type, the modelLoader and the params. The modelLoader property defines whether an MVC or a simple model must be loaded. The type property defines which class must be used for that model using an AMD module identifier and finally the params property content is passed to the model class constructor to build an instance.
"models": {
"model1": {
"modelLoader": "dojox/app/utils/mvcModel",
"type": "dojox/mvc/EditStoreRefListController",
"params":{
"store": {"$ref":"#stores.namesStore"}
}
},
"model2": {
"modelLoader": "dojox/app/utils/simpleModel",
"params":{
"store": {"$ref":"#stores.namesStore"}
}
}
}
All model modules that are used must also be explicitly listed in the dependencies property.
defaultView¶
String. Mandatory. The name of the view (or views) to load when the application is initialized. Multiple views can be included in the DefaultView in the config, this allows multiple views to be displayed with different constraints (or regions) at the same time. It is also now possible to transition views in regions other than the center. To specify multiple views, the view names would listed separated by a “+”, for example: “view1+view2” or “view1,subviewA+view2”.
"defaultView": "header+navigation+TestInfo"
defaultTransition¶
String. Optional. The default animation type for the view transition, the defaultTransition is only used if transition is not set in the config and it is not set or defaulted on the transitionEvent
"defaultTransition": "slide"
transition¶
String. Optional. The transition animation type to use for the view transition. If a transition is set on a view or parent it will override the transition set on the transitionEvent or the defaultTransition in the config.
"transition": "slide"
has¶
Object. Optional. The has sections are used to merge sections of config from the has sections into the final config based upon has tests. The has sections will include a string which is used as a has test, if the has test for the string is true the section below that string will be merged into the config at the same level as the has section. A ”!” can be used to indicate that a section should be merged if the has test is false. If the has section to be merged contains a property which already exists at that level of the config, the value from the has section will replace the value in the config, if the has section contains an array which also exists in the config at the same level as the has section the items from the array in the has section will be added to the array in the config. As an example:
//if the app had code like this:
require(["dojo/text!"+configurationFile], function(configJson){
var config = json.fromJson(configJson);
var width = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
if(width <= 600){
has.add("phone", true);
}
has.add("ie9orLess", has("ie") && (has("ie") <= 9));
Application(config);
});
//the config could have a has section like this:
"has" : {
"phone" : {
"defaultView": "configuration"
},
"!phone" : {
"defaultView": "configuration+TestInfo"
},
"ie9orLess" : {
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/HistoryHash"
]
},
"!ie9orLess" : {
"controllers": [
"dojox/app/controllers/History"
]
}
},
views¶
- Object. Mandatory if there are views. The child views of an application or of a view. Dependencies may be defined on views for optimization and organization purposes. Models might also be defined on views if they are view-specific. Finally a view item as five additional properties:
- “template” for defining the view rendering for views of type
dojox/app/View - “controller” to provide an AMD module to be mixed into the view as the view controller. In 1.9 the option to be able to load a default controller has been removed, the controller must be specified for a view in order to be loaded. If the view does not have a controller module to load, it should not set a controller, as of 1.9 setting the controller to “none” is no longer supported.
- “transition” for optional view-specific transitions
- “nls” for optionally defining an internationalisation AMD root module for the view of type
dojox/app/View. Per Dojo loader specifications the path to the module must contain “/nls/”. Once done the view template can use the ${nls.nlskey} notation instead of english text to automatically use the text translated in the right language. - “type” a reference to an AMD module defining an alternate view type extending
dojox/app/ViewBase.
- “template” for defining the view rendering for views of type
AMD modules identifiers starting with “.” will be resolved relative to the application root. All other modules identifiers will be resolved according to the Dojo AMD loader rules and in particular with respect to its configuration provided as part of the loaderConfig attribute.
"views": {
// simple view without any children views
// views can has its own dependencies which will be loaded
// before the view is first initialized.
"home": {
"dependencies":[
"dojox/mobile/RoundRectList",
"dojox/mobile/ListItem",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeCategory"
],
"controller": "./views/simple/home.js ",
"template": "./views/simple/home.html"
},
// simple composite view which loads all views and shows the default
"main":{
// all views in the main view will be bound to the user model
"models": [],
"controller": "simple.js",
"template": "simple.html",
"defaultView": "main",
"defaultTransition": "slide",
// the child views available to this view
"views": {
"main":{
"template": "./views/simple/main.html",
"nls": "./nls/simple/main"
},
"second":{
"controller": "./views/simple/second.js",
"template": "./views/simple/second.html"
},
"third":{
"controller": "./views/simple/third.js",
"template": "./views/simple/third.html",
"type": "mypackage/MyDtlView"
}
},
"dependencies":[
"dojox/mobile/RoundRectList",
"dojox/mobile/ListItem",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeCategory",
"dojox/mobile/EdgeToEdgeList"
]
},
"repeat": {
// model declared at view level will be accessible to this view
// or its children.
"models": {
"repeatmodels": {
"params":{
"store": {"$ref":"#stores.repeatStore"}
}
}
},
"controller": "./views/repeat.js",
"template": "./views/repeat.html",
"dependencies":["dojox/mobile/TextBox"]
}
}
This configuration serves two purposes configuring the application within the client without having to do it by code and help building the application for production.
The main dojox/app modules¶
dojox/app is built around the following focused core modules that can be used in the configuration file:
dojox/app/main is used to create a dojox/app Application object from the JSON configuration. The main responsibilities of dojox/app/main include loading the various controllers & data stores as well as managing the application lifecycle.
dojox/app/View provides a view object in charge of the view rendering and lifecycle. It contains a template string which will be rendered. A view can itself have nested View objects.
dojox/app/Controller a base class for the various application controllers:
dojox/app/controllers/Layouta controller that performs nested view layoutdojox/app/controllers/Loada controller that loads the view templates and view controller modulesdojox/app/controllers/Historya controller that maintains application history using HTM5 history API. This will not work on platforms that don’t support it like IE, Android 3 & 4, iOS 4.dojox/app/controllers/HistoryHashan alternate controller that maintains application history using URL hash. It works on all browsers but has limitations with regard to browser refresh and going back to an URL out of application’s history stack.
dojox/app/module a package containing various modules than can be used in the configuration file to be mixed into the Application object.
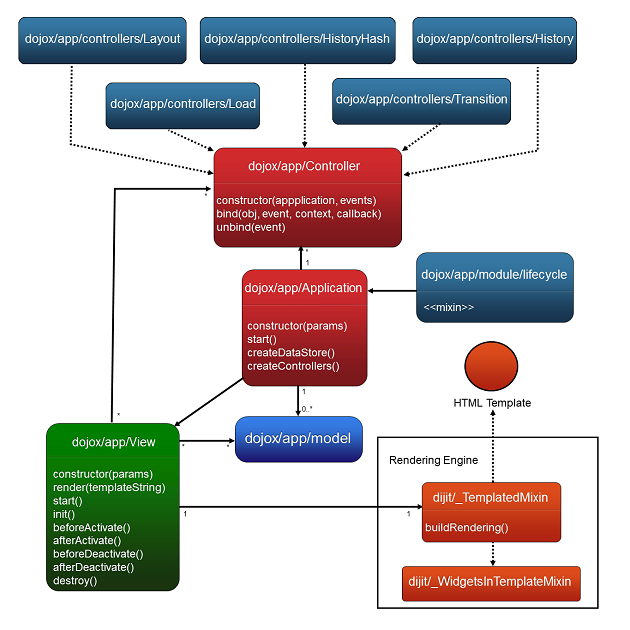
The following diagram represents the high level architecture of dojox/app and in particular how the modules listed
above interacts each others:
Comparison with dojox/mobile/app¶
First please note that dojox/mobile/app has been deprecated in favor of dojox/app, so you are fully encouraged to use dojox/app.
The main differences between dojox/app and dojox/mobile/app are the following:
dojox/appenables the model bindingdojox/appuses view structure to enable the nested views using a composite design pattern.dojox/mobile/appwill require additional code for that.dojox/appcontains the layout mechanism to ensure the content at different application/view level work well togetherdojox/mobile/appmanages the navigation history in StageController by using a history stack. Dojox/app provides both HTML5 pushState & history stack for managing the navigation history.