Data Handlers¶
| Authors: | Yoshiroh Kamiyama |
|---|
Contents
- Data Handlers
- The DataHandler Class
- The FileTypeMap Interface
- The DataSource Interface
- The ContentTypeMap Class
- The ContentHandler Interface
- The Overall Control-Flow
- How to replace DataHandler
- How to replace FileTypeMap
- How to replace DataSource
- How to replace ContentTypeMap
- How to override ContentType
- How to register ContentType
- How to register ContentHandler
- Lazy-loading of widget code
- Script execution
- How to open an external view programmatically
Dojo Mobile has the ability to load external view content and create a new target view dynamically. The _ItemBase class, a base class of ListItem, IconItem, etc., has the ‘url’ property, which allows you to specify a URL of external data that will be a new view content after performing a view transition. Two data formats, HTML and JSON, are supported, and their content handlers are implemented in dojox/mobile/ViewController. (See also Dynamic Content Loading for details.)
The module dojox/mobile/ViewController modularizes the handlers to allow the user to customize them. The data handlers are structured as follows:
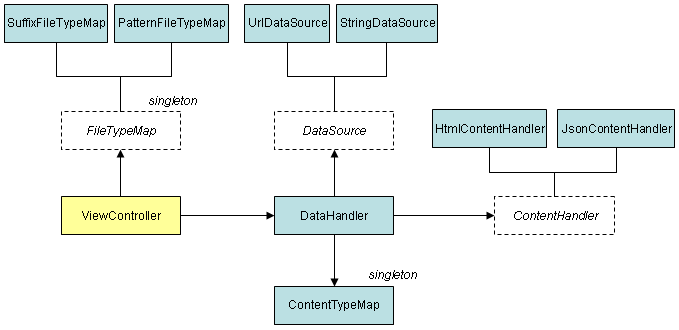
The data handlers consist of the following components:
- DataHandler
- FileTypeMap
- DataSource
- ContentTypeMap
- ContentHandler
All of the above components are loaded dynamically at run-time. You do not need to explicitly require them in your application. If your application does not use the “url” property of _ItemBase, they will not be loaded.
The DataHandler Class¶
The DataHandler component provides an interface between content data and a ContentHandler. It fetches content data through DataSource and calls ContentHandler to parse the content data and create a new view. The DataHandler is called from ViewController.
The FileTypeMap Interface¶
FileTypeMap provides a map for determining content-type from the URL of the content data. Two actual modules are available: SuffixFileTypeMap and PatternFileTypeMap. SuffixFileTypeMap, which is the default module, determines content-type from a suffix
of the given URL. PatternFileTypeMap determines content-type by pattern-matching against the given URL.
The DataSource Interface¶
DataSource encapsulates access to data. Two actual modules are available: UrlDataSource and StringDataSource. UrlDataSource, which is the default module, accesses the given URL and fetches the data as text. StringDataSource simply returns the given text.
The ContentTypeMap Class¶
ContentTypeMap provides a map for determining the content-handler class from a content-type. The dojox/mobile/dh/ContentTypeMap class is a singleton class.
The ContentHandler Interface¶
ContentHandler is responsible for parsing the given data and creating a new view at the specified position. Three actual modules are available: HtmlContentHandler, HtmlScriptContentHandler, and JsonContentHandler. HtmlContentHandler handles HTML fragment content. In the HTML fragment, the top level must be a View widget or one of its subclasses. HtmlScriptContentHandler also handles HTML fragments and has the ability to execute inline script code.
The Overall Control-Flow¶
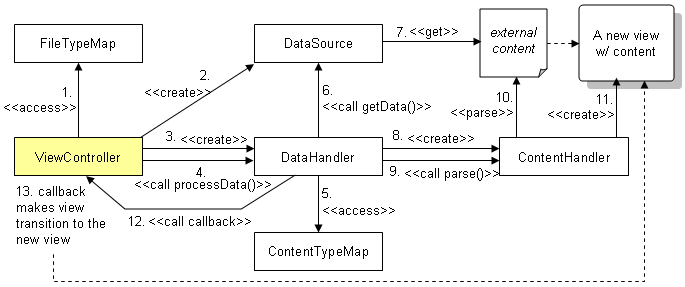
- ViewController accesses FileTypeMap to get a content type (e.g. “html” or “json”) from the file name suffix.
- ViewController creates a DataSource with the url property.
- ViewController creates a DataHandler for the created DataSource.
- ViewController calls DataHandler.processData() with the content type.
- DataHandler accesses ContentTypeMap to get a ContentHandler class name for the given content type.
- DataHandler calls DataSource.getData().
- DataSource gets the external content.
- DataHandler creates the ContentHandler class.
- DataHandler calls ContentHandler.parse() to parse the content.
- ContentHandler.parse() parses the content.
- ContentHandler.parse() creates a new view.
- DataHandler calls a callback that is defined in ViewController.
- The callback performs a view transition to the new view.
How to replace DataHandler¶
The default DataHandler class name is “dojox/mobile/dh/DataHandler”, which is defined as a dataHandlerClass property in ViewController. It can be overridden by adding the dataHandlerClass property to the transitionOptions. Below is an example of specifying your own DataHandler in ListItem.
<li data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/ListItem" data-dojo-props='url:"data/view1.html",
transitionOptions:{dataHandlerClass:"com/acme/MyDataHandler"}'>
External View #1
</li>
How to replace FileTypeMap¶
The default FileTypeMap class name is “dojox/mobile/dh/SuffixFileTypeMap”, which is defined as a fileTypeMapClass property in ViewController. It can be overridden by adding the fileTypeMapClass property to the transitionOptions. Below is an example of specifying your own FileTypeMap in ListItem.
<li data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/ListItem" data-dojo-props='url:"data/view1.html",
transitionOptions:{fileTypeMapClass:"com/acme/MyFileTypeMap"}'>
External View #1
</li>
How to replace DataSource¶
The default DataSource class name is “dojox/mobile/dh/UrlDataSource”, which is defined as a dataSourceClass property in ViewController. It can be overridden by adding the dataSourceClass property to the transitionOptions. Below is an example of specifying your own DataSource in ListItem.
<li data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/ListItem" data-dojo-props='url:"data/view1.html",
transitionOptions:{dataSourceClass:"com/acme/MyDataSource"}'>
External View #1
</li>
How to replace ContentTypeMap¶
Usually, ContentTypeMap does not need to be replaced. If you have your own DataHandler, however, you can have your own ContentTypeMap as well, since DataHandler depends on ContentTypeMap.
How to override ContentType¶
Usually, content type is determined by looking up the matching entry in a ContentTypeMap. If you want to skip the look-up, and explicitly specify a particular content type, you can provide the contentType property to the transitionOptions. Below is an example of specifying a content type in ListItem.
<li data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/ListItem" data-dojo-props='url:"data/view1.data",
transitionOptions:{contentType:"data"}'>
External View #1
</li>
How to register ContentType¶
Content type is determined by a FileTypeMap. For example, SuffixFileTypeMap uses the file name suffix to determine content type. For SuffixFileTypeMap, you can register “suffix to content type” entries into the map. SuffixFileTypeMap is a singleton module. You can simply get its module return value and use the add() method to register your entries.
require([
"dojox/mobile/dh/SuffixFileTypeMap",
"dojox/mobile/parser",
"dojox/mobile",
"dojox/mobile/compat"
], function(SuffixFileTypeMap){
SuffixFileTypeMap.add("acme", "data"); // regard *.acme as "data" type
});
If a given suffix does not match any of the entries in the map, ViewController uses “html” as the default content type.
How to register ContentHandler¶
Which ContentHandler to use is decided by ContentTypeMap. In your application, you can register “content type to content handler class” entries into the map. ContentTypeMap is a singleton module. You can simply get its module return value and use the add() method to register your entries.
require([
"dojox/mobile/dh/ContentTypeMap",
"dojox/mobile/parser",
"dojox/mobile",
"dojox/mobile/compat"
], function(ContentTypeMap){
ContentTypeMap.add("html", "dojox/mobile/dh/MyHtmlContentHandler");
});
Lazy-loading of widget code¶
The widget code used in external content does not need to be loaded and made available before creating the external view. Both HtmlContentHandler and JsonContentHandler support the dynamic loading of the necessary widget code. You do not have to explicitly require widget code that will be used in external views.
Script execution¶
The HtmlScriptContentHandler handler allows you to have <script> tags in an external content. If you use relative path, such as src=”hello.js”, the path is relative from your application’s main html page. You can place <script> tags anywhere you like, since all the <script> blocks are removed from html text before creating DOM elements.
You can change the default content handler for html to HtmlScriptContentHandler as shown in the example below.
require([
"dojox/mobile/dh/ContentTypeMap",
"dojox/mobile/parser",
"dojox/mobile",
"dojox/mobile/compat"
], function(ContentTypeMap){
ContentTypeMap.add("html", "dojox/mobile/dh/HtmlScriptContentHandler");
});
<div id="view1" data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/View">
<script src="hello.js"></script>
<script>
alert("hi");
</script>
<h1 data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/Heading">Example</h1>
....
</div>
How to open an external view programmatically¶
You can programmatically open an external view without relying on the _ItemBase class by using the openExternalView() method of the ViewController. See examples of dojox/mobile/ViewController for details.
Table of Contents
- Data Handlers
- The DataHandler Class
- The FileTypeMap Interface
- The DataSource Interface
- The ContentTypeMap Class
- The ContentHandler Interface
- The Overall Control-Flow
- How to replace DataHandler
- How to replace FileTypeMap
- How to replace DataSource
- How to replace ContentTypeMap
- How to override ContentType
- How to register ContentType
- How to register ContentHandler
- Lazy-loading of widget code
- Script execution
- How to open an external view programmatically