dojox/app/controllers/History(Hash)¶
| since: | V1.8 |
|---|
dojox/app/controllers/History and dojox/app/controllers/HistoryHash control forward and backward navigation between views.
A view can use transitionOptions or href to navigate forward or backward. dojox/app/controllers/History leverages HTML5 history API for this while dojox/app/controllers/HistoryHash uses url hashes.
HTML5 history does not work on Android 3.x and 4.x, iOS 4.x and old desktop browsers. On these platforms you must use hash history instead.
Usage¶
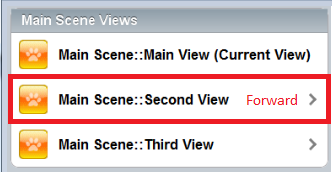
transitionOptions can be used on any dojox/mobile widgets which inherit from dojox/mobile/_ItemBase. The following sample will result in a transition to the ‘second’ view from the ‘main’ view of the application.
<li data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/ListItem"
data-dojo-props="iconPos:'0,0,29,29', clickable: true,
transitionOptions: {target:'main,second', url: '#main,second', params : {'cursor':index}}">
Main Scene::Second View
</li>
Transition Attributes¶
target¶
String. The target view or scene id path. Note the value for the target|String should be the complete id path from its ancestor scene to the leaf view.
url¶
String. The url that will be used to update the location value in browser’s address bar after the transition.
params¶
Object. Application data to be passed to the view on the transition, it can be referenced in the view with this.params["paramName"].
title¶
String. Reserved for future use.
Forward Transition Using href¶
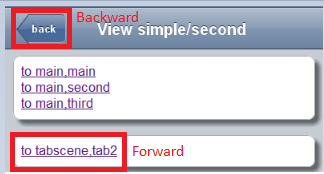
Besides the transitionOptions on mobile widgets, the href attribute in a hyperlink can also start the transition in dojox/app. The following HTML snippet results in a transition to the ‘main’ view of ‘main’ scene.
<a href="#main,main">to main,main</a>
Backward Transition¶
To start the backward transition, all we need to do is to add a back button on the Heading widgets of dojox/mobile. The back attribute declares the back button label on the heading in the following sample.
<h1 data-dojo-type="dojox/mobile/Heading" data-dojo-props="back:'Home'">Data Binding Example</h1>
If you need to achieve this by code call the back method on history:
history.back();